ENERGIASALV
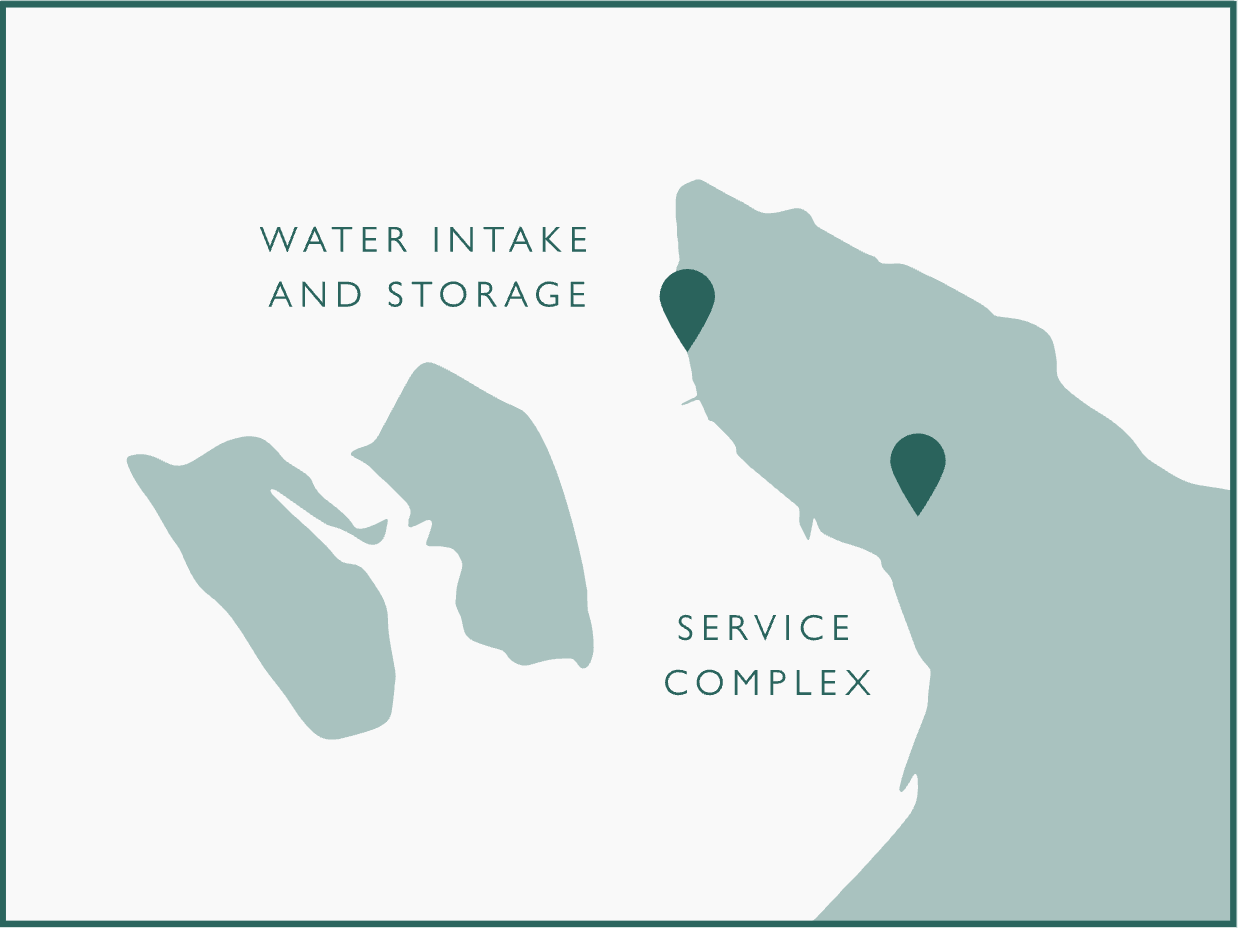
Energiasalv is a 500 MW underground battery to be built in Paldiski. When renewable energy is produced more than is consumed, Energiasalv stores renewable energy by pumping water from underground reservoirs into Paldiski Bay. If there is less wind and solar energy than consumers need, Energiasalv provides electricity to the power grid by releasing water from Paldiski Bay into underground reservoirs.
Energiasalv provides 15 million kWh of previously stored electricity to the grid during its nominal operating cycle of 30 hours, which is more than the average daily electricity consumption of all Estonian households. Energiasalv Zero Terrain pumped hydro energy storage technology is currently the most affordable solution for controlled electricity generation and storage in the world. Its introduction will significantly reduce the price of peak energy and thereby reduce the cost of electricity for households and businesses world’s most affordable solution for controlled electricity generation and storage.
Energiasalv Paldiski follows the Green Tiger Energy Roadmap.
Energiasalv successfully fulfills the three goals of the energy trilemma
Energy security
Energiasalv provides 15 million kWh of previously stored electricity to the grid during its nominal operating cycle of 30 hours, which is more than the average daily electricity consumption of all Estonian households.
Affordable price
Energiasalv water storage technology is currently the most affordable technological solution for controlled electricity generation and storage in the world, the introduction of which will significantly reduce the electricity price of peak energy and thereby reduce the cost of electricity for households and businesses.
Minimal impact on the environment
Energiasalv's energy solutions align with environmental and social responsibilities by storing only renewable energy, thereby reducing dependence on unethical production practices and fossil fuels.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions about the Energiasalv Paldiski.